Note
Click here to download the full example code
2.1.4. Two pulse interaction in a NLPM750 PCF¶
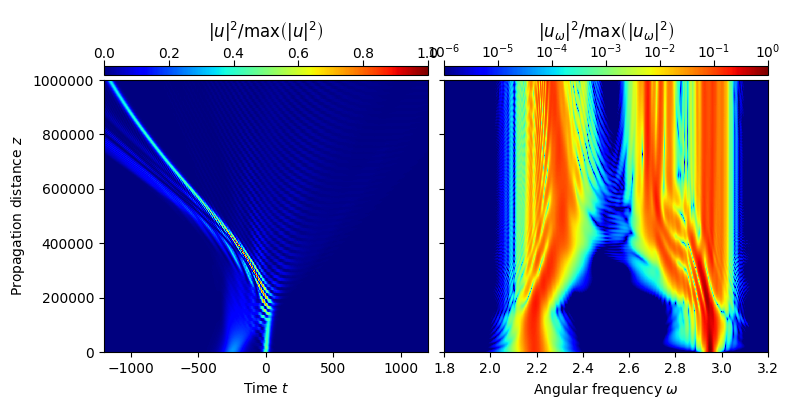
This examples demonstrates the interaction between a fundamental soliton and a dispersive wave in a NL-PM-750 photonic crystal fiber. For the numerical simualtion the forward model for the analytic signal including the Raman effect is used [3].
In particular, this example reproduces the propagation scenario for \(t_0=250\,\mathrm{fs}\), shown in Fig.~2(b) of Ref. [2]. Note that here we use a polynomial expansion of the propagation constant, obtained for the reference frequency \(\omega_{\rm{ref}}=1.85\,\mathrm{rad/fs}\). For a more detailed discussion, see Ref. [2].
- References:
[1] A. Demircan, Sh. Amiranashvili, C. Bree, C. Mahnke, F. Mitschke, G. Steinmeyer, Rogue wave formation by accelerated solitons at an optical event horizon, Appl. Phys. B 115 (2014) 343, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5609-9
[2] O. Melchert, C. Bree, A. Tajalli, A. Pape, R. Arkhipov, S. Willms, I. Babushkin, D. Skryabin, G. Steinmeyer, U. Morgner, A. Demircan, All-optical supercontinuum switching, Communications Physics 3 (2020) 146, https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-020-00414-1.
import fmas
import numpy as np
from fmas.grid import Grid
from fmas.models import FMAS_S_R
from fmas.solver import IFM_RK4IP
from fmas.analytic_signal import AS
from fmas.propagation_constant import PropConst
from fmas.tools import change_reference_frame, plot_evolution
def define_beta_fun_poly_NLPM750():
# -- EXPANSION COEFFIENTS
coeffs =[-7.47658629e-08, 2.07925891e-06, -2.50978046e-05, 1.70783580e-04,
-7.06498505e-04 , 1.74251689e-03 , -2.05510570e-03, -1.02991785e-03,
7.44467252e-03, -1.15714412e-02, 1.06894885e-02, -1.03866947e-02,
1.11828958e-02, 8.28155802e-04 , -1.51886109e-02 , 4.97000000e+00,
8.90000000e+00]
# -- FREQUENCY FOR WHICH EXPANSION COEFFICIENTS ARE VALID
w_ref = 1.85 # (rad/fs)
# -- PROPAGATION CONSTANT FOR DETUNING (1/micron)
_beta = np.poly1d(coeffs);
return lambda w: _beta(w-w_ref)
def main():
# -- DEFINE SIMULATION PARAMETERS
# ... COMPUTATIONAL DOMAIN
t_max = 2000. # (fs)
t_num = 2**13 # (-)
z_max = 1.0e6 # (micron)
z_num = 10000 # (-)
z_skip = 10 # (-)
n2 = 3.0e-8 # (micron^2/W)
c0 = 0.29979 # (fs/micron)
lam0 = 0.860 # (micron)
w0_S = 2*np.pi*c0/lam0 # (rad/fs)
t0_S = 20.0 # (fs)
w0_DW = 2.95 # (rad/fs)
t0_DW = 70.0 # (fs)
t_off = -250.0 # (fs)
sFac = 0.75 # (-)
beta_fun = define_beta_fun_poly_NLPM750()
pc = PropConst(beta_fun)
# -- INITIALIZATION STAGE
grid = Grid( t_max = t_max, t_num = t_num, z_max = z_max, z_num = z_num)
model = FMAS_S_R(w=grid.w, beta_w=pc.beta(grid.w), n2 = n2)
solver = IFM_RK4IP( model.Lw, model.Nw, user_action = model.claw)
# -- SET UP INITIAL CONDITION
t = grid.t
A0 = np.sqrt(abs(pc.beta2(w0_S))*c0/w0_S/n2)/t0_S
A0_S = A0/np.cosh(t/t0_S)*np.exp(1j*w0_S*t)
A0_DW = sFac*A0/np.cosh((t-t_off)/t0_DW)*np.exp(1j*w0_DW*t)
Eps_0w = AS(np.real(A0_S + A0_DW)).w_rep
solver.set_initial_condition( grid.w, Eps_0w)
solver.propagate( z_range = z_max, n_steps = z_num, n_skip = z_skip)
# -- SHOW RESULTS
utz = change_reference_frame(solver.w, solver.z, solver.uwz, pc.vg(w0_S))
plot_evolution( solver.z, grid.t, utz, t_lim=(-1200,1200), w_lim=(1.8,3.2))
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 44.519 seconds)